In the realm of communication, where language meets innovation, the Morse Code System stands as a testament to the ingenuity of human ingenuity.
Crafted with dots and dashes, this system of encoding and decoding messages has played a pivotal role in shaping history. As we delve into the intricate world of Morse Code, we uncover not only a means of communication but a fascinating language with its own set of rules and nuances.
This Morse Code Translator guide invites you to explore the captivating journey of Morse Code, where seemingly simple arrangements of dots and dashes carry profound messages.
From its origins to its instrumental role in maritime and telecommunication history, the Morse Code has left an indelible mark on conveying information.
Join us in unraveling the exciting facts and untold stories behind the Morse Code System. Whether you’re a language enthusiast, a history buff, or intrigued by the evolution of communication, this guide aims to illuminate the unique and enduring significance of Morse Code in the tapestry of human communication.
Let’s embark on a journey to decode the dots and dashes that have echoed across time.
What is Morse Code?
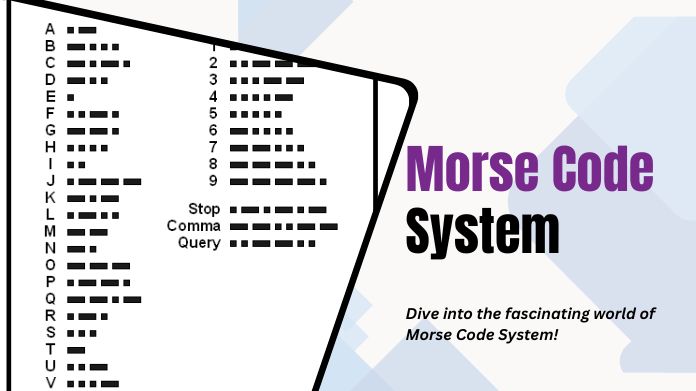
Morse Code is a form of communication that utilizes a series of dots and dashes to represent letters and numbers. Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail developed it in the early 1830s using telegraph systems to send messages over long distances.
Each letter and number is represented by a unique combination of short signals (dots) and long signals (dashes). Morse Code has been widely used for communication in various fields, such as military, maritime, and aviation.
While it is less commonly used today due to technological advancements, the Morse Code still holds historical significance. It is sometimes used in specific applications, such as amateur radio operations and emergencies.
Facts About the Morse Code System
1. Inventive Origins
Developed by Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail in the early 1830s, the Morse Code was initially conceived as a long-distance telegraph communication.
The system’s inventors ingeniously assigned shorter sequences to more frequently used letters, optimizing its efficiency.
2. Universal Adoption
Morse Code’s versatility led to widespread adoption across diverse fields, including maritime, aviation, and military communications.
Its simplicity and reliability made it a valuable tool for transmitting messages, especially in challenging environments.
3. SOS Distinction
Contrary to popular belief, the SOS distress signal was not chosen for its meaning but for its distinctive and easily recognizable pattern (dot-dot-dot, dash-dash-dash, dot-dot-dot). It became synonymous with emergency calls at sea.
4. Linguistic Adaptation
Beyond English, Morse Code has been adapted for various languages and scripts. This adaptability allowed it to bridge linguistic barriers, making it a truly international mode of communication.
5. An Artistic Influence
Morse Code’s impact extends beyond communication; it has inspired artistic expressions, with artists using its patterns and symbolism in visual arts, music, and literature. This fusion of technology and art showcases its enduring cultural influence.
6. Enduring Relevance
Despite advancements in technology, Morse Code remains relevant. Ham radio operators, enthusiasts, and emergency responders continue to use it, emphasizing its resilience and timeless utility in modern times.
Application of Morse Code System
The Morse Code system is a method of communication that uses a sequence of dots and dashes to represent letters, numbers, and punctuation marks.
Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail developed it in the early 1830s, and it was primarily used for long-distance communication before the advent of the telegraph.
The Morse Code system is based on a simple binary code, with dots representing short signals and dashes representing longer signals. Each letter of the alphabet, as well as numbers and punctuation marks, is assigned a unique combination of dots and dashes.
For example, “A” is represented by a dot followed by a dash, while “B” is represented by a dash followed by three dots. The Morse Code system has been used in various applications throughout history.
Telegraph operators commonly used it to send messages over long distances using telegraph wires. Pilots and navigators also used it to communicate distress signals in emergencies.
Additionally, the Morse Code system has been used by the military for covert communication purposes, as well as by amateur radio operators for recreational communication.
While the Morse Code system has become less common in modern times with the advancement of technology, it still holds historical and cultural significance.
It is considered a valuable skill for amateur radio operators and is even taught in some schools as part of history or communication courses.
The system’s simplicity and efficiency have made it an enduring method of communication, and it continues to be recognized and appreciated by enthusiasts worldwide.
Conclusion
The Morse Code System, born out of the quest for efficient communication, has etched its name in history with a legacy that spans centuries.
As we appreciate the dots and dashes that convey messages across time and space, Morse Code stands not just as a system but as a testament to the indomitable spirit of human innovation.
Let’s continue to decode the fascinating history and untold stories hidden within this extraordinary communication language.
