Morse Code work transcends linguistic boundaries as a universal communication system with its rhythmic arrangement of dots and dashes.
Originating in the early 19th century, Morse Code was initially designed for the English language. However, its simplicity and adaptability have led to its widespread use in various languages worldwide.
This morse code translator exploration delves into the fascinating realm of “How Does Morse Code Work in Other Languages.” As we unravel the intricacies of this timeless communication method, we will discover how Morse Code has seamlessly adapted to convey messages in diverse linguistic landscapes.
Join us on this journey to understand the versatility of Morse Code and its ability to transcend the confines of language, connecting people across cultures through a series of dots and dashes.
How Was Morse Code Created?
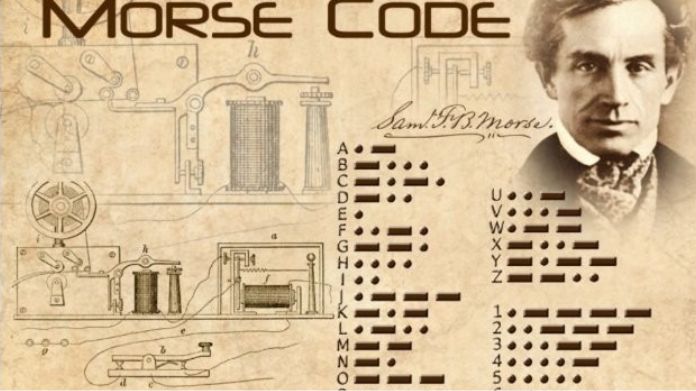
Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail created the Morse Code in the 1830s and 1840s. They developed the code to communicate for the newly invented telegraph. Morse Code uses a sequence of dots and dashes to convey letters and numbers.
The code was based on the frequency of letters in English, with more frequently used letters assigned shorter codes. This allowed for more efficient communication over long distances using the telegraph system. Morse Code quickly became widely adopted and was used extensively in telegraph communication for many years.
It played a crucial role in communication during World War II and was later replaced by more modern communication technologies. However, amateur radio operators still use Morse Code today, which is considered an essential part of telecommunications history.
How Does Morse Code Work?
Morse code is a communication system that uses dots and dashes to convey letters and numbers. Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail invented it in the 1830s and 1840s for use with the telegraph machine.
In Morse code, each letter of the alphabet, numbers, and some special characters are represented by a series of dots and dashes. The dots are short signals, and the dashes are longer signals. These signals can be transmitted using sound, light, or electrical impulses.
To send a message in Morse code, the sender uses a signaling device, such as a telegraphy machine or a flashlight, to create the dots and dashes. The receiver then decodes the dots and dashes them into letters and numbers using a chart or listening to the signals.
Morse code work is still used today, although it is less common than it once was. It is often used when other forms of communication are not possible, such as in emergencies or military operations. It is also used by amateur radio operators and in some aviation and maritime communication systems.
How Does Morse Code Work in Other Languages?

Morse Code, named after its inventor, Samuel Morse, is a method of communication that employs a series of dots and dashes to represent letters and numbers. Initially developed for the English language, Morse Code has also been adapted to work in other languages.
Some modifications need to be made to use Morse Code in different languages. This is because each language has its own unique set of characters and sounds. For example, in English, Morse Code uses five essential elements: dot, dash, space, short gap, and long gap. However, other languages may require additional elements or variations.
Additional characters and symbols can be added to represent specific sounds or letters to adapt Morse Code to different languages. These modifications allow Morse Code to effectively represent other languages’ sounds and characters effectively.
Furthermore, Morse Code can also transmit non-English words or phrases by spelling them out using the appropriate Morse Code characters for each letter. This makes it possible to communicate in different languages using Morse Code, albeit with some modifications and adaptations.
Overall, Morse Code is a versatile method of communication that can be adapted to work in different languages by adding or modifying characters and symbols. This allows individuals to use Morse Code to communicate in languages other than English.
Final Note
So, that’s a wrap on Morse Code and its magic in different languages. From English to languages worldwide, those dots and dashes know how to bridge the communication gap. Morse Code is like a secret language everyone can understand, making it a timeless way to send messages no matter where you are.
The simplicity of dots and dashes becomes a universal code connecting us all. Hats to Morse Code for keeping communication simple, no matter the language!
