Using dots and dashes to convey messages, Morse code alphabets has played a crucial role in history and modern technology.
When Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail created the Morse code in the early 1830s, it was first applied to long-distance telegraphy communications.
It has been used in many industries, such as amateur radio operations, aviation, and maritime communication. Acquiring knowledge of Morse code can be an exciting pursuit, providing a distinctive means of communication.
In this Morse code translator guide, we will deconstruct the Morse code alphabet and offer a simple, organized way to comprehend this age-old form of communication.
What is Morse Code?
The Morse code is named for Samuel Morse, who, along with Alfred Vail, was instrumental in its development. Its primary purpose during the 19th century was to be used in telegraphy, a new kind of long-distance communication.
The code was an essential tool for swiftly transmitting messages over long distances due to its simplicity and efficacy. Early telegraphy made extensive use of Morse code, which allowed for the quick transfer of information throughout the US and, eventually, the rest of the world.
It was essential in establishing connections between citizens, companies, and governments. But as technology developed, telegraphy was replaced by more sophisticated means of communication like the internet and telephony.
Despite this change, Morse code things is still in use today. Instead, it has found niche applications in various fields, such as aviation, maritime, and amateur radio operations. Pilots, sailors, and amateur radio enthusiasts continue to use Morse code as a reliable means of communication.
Basics of Morse Code
The two fundamental components of Morse code are dots (·) and dashes (–). Letters, numerals, and other symbols are represented by combining these elements.
Here’s a basic explanation.
- A symbol (·) stands for the letter “E.”
- A symbol (–) stands for the letter “T.”
- Spaces are used to separate characters, with each space representing one dot.
- Spaces the length of seven dots are used to indicate gaps between words.
After going over the essentials, let’s take a closer look at the Morse code alphabet.
What is the Morse Code Alphabet?

Letters and Numerals
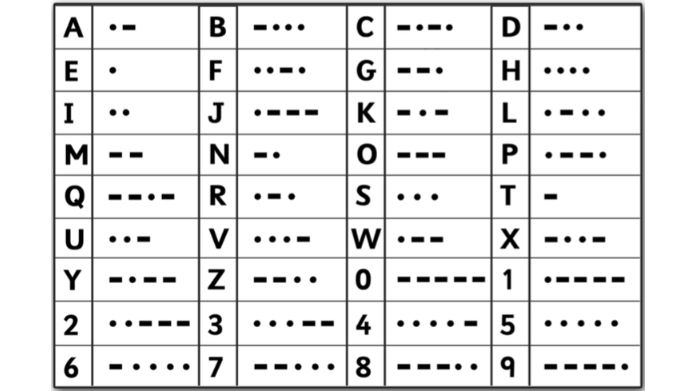
Every letter in the English alphabet and the numbers 0–9 has a different set of dots and dashes in the Morse code alphabet. This is the entire alphabet in Morse code.
- A: · –
- B: – · · ·
- C: – · – ·
- D: – · ·
- E: ·
- F: · · – ·
- G: – – ·
- H: · · · ·
- I: · ·
- J: · – – –
- K: – · –
- L: · – · ·
- M: – –
- N: – ·
- O: – – –
- P: · – – ·
- Q: – – · –
- R: · – ·
- S: · · ·
- T: –
- U: · · –
- V: · · · –
- W: · – –
- X: – · · –
- Y: – · – –
- Z: – – · ·
- 0: – – – – –
- 1: · – – – –
- 2: · · – – –
- 3: · · · – –
- 4: · · · · –
- 5: · · · · ·
- 6: – · · · ·
- 7: – – · · ·
- 8: – – – · ·
- 9: – – – – ·
Punctuation Marks
Morse code includes representations for common punctuation marks, symbols, and letters and numbers.
- . (Period): · – · – · –
- , (Comma): – – · · – –
- ? (Question Mark): · · – – · ·
- ‘ (Apostrophe): · – – – – ·
- ! (Exclamation Point): – · – · – –
- / (Slash): – · · – ·
- ( (Parenthesis – Open): – · – – ·
- ) (Parenthesis – Close): – · – – · – –
- & (Ampersand): · – · · ·
- : (Colon): – – – · · ·
- ; (Semicolon): – · – · – ·
- = (Equal Sign): – · · · –
- (Plus Sign): · – · – ·
- (Hyphen): – · · · · –
- ” (Quotation Marks): · – · · – ·
- @ (At Symbol): · – – · – ·
Prosigns and Procedural Signals
Additionally, “prosigns,” or unique signals, are included in Morse code and utilized for signalling and procedural purposes. Among them are.
- AR (End of Message): · – · – · –
- AS (Wait): · – · · – ·
- BK (Break): – · · · – · –
- KN (End of Transmission): – · – · – ·
- SK (End of Work): · · · – · ·
How to Learn Morse Code?
Below are some easy methods to understand Morse code effectively. Here are the methods.
1. Traditional Methods: Learning Morse code traditionally involves learning the dots and dashes for every letter, number, and symbol. Although it can take some time, practice and repetition are frequently used. Flashcards, Morse code charts, and listening to Morse code transmissions are popular methods for learning the code.
2. Modern Approaches: Many contemporary tools and resources are available in the digital age to help learn Morse code more quickly.
3. Apps for Morse Code: Many smartphone applications offer practice exercises and interactive lessons for Morse code.
4. Online Courses: Various websites and online learning environments provide interactive exercises, educational videos, and courses on Morse code.
5. Morse Code Keyers: These gadgets have adjustable speeds and can produce Morse code signals for practice.
Tips to Learn Morse Code
Regardless of your approach, here are some valuable hints for learning Morse code.
1. Commence with the Fundamentals: Before learning numbers and punctuation, familiarize yourself with the Morse code alphabet.
2. Practice Frequently: Maintaining your proficiency in Morse code requires consistent practice. Every day, set aside time for training.
3. Increase Speed Gradually: As you get more comfortable, start with slow Morse code transmissions and progressively pick up the pace.
4. Take Part in a Community: Joining an online Morse code community or ham radio club can be a great way to practice and connect with other enthusiasts.
How to Use Morse Code?
1. Ham Radio Operations
Morse code is widely used by amateur radio operators, or “hams,” as a communication tool. It makes long-distance communication possible with little equipment. Many hams use Morse code for informal conversations or competitions because they find it nostalgic and challenging.
2. Emergency Signaling
In emergencies where other means of communication may be compromised, Morse code can be an invaluable tool. Distress signals, like SOS (· · · – – – · · ·), are recognized globally and can be transmitted via radio transmissions, flashlight signals, or sound signals.
3. Fun and Games
Even outside of its valuable uses, Morse code can be entertaining. Some people like translating well-known quotes and texts into Morse code, making Morse code puzzles or even sending covert messages to loved ones.
Conclusion
The skill of Morse code may seem archaic in the era of instantaneous digital communication. Nonetheless, it’s practical because of its historical significance and ongoing applicability in particular fields.
Acquiring proficiency in the Morse code alphabet and applying it can be demanding yet fulfilling. Remember the simplicity of the dots and dashes as you begin your journey to learn Morse code, and be grateful for the Part it played in the past in bringing people and nations together.
Morse code provides a fascinating window into our technological past, whether you’re a ham radio enthusiast, an adventurer visiting far-flung locations, or just interested in learning more about this unusual mode of communication.
So, grab your flashlight, keyer, or smartphone app, and start decoding the hidden language of Morse code. You might discover a new way to connect with the world and share in the rich tapestry of human communication.
