Morse code, with its rhythmic pattern of dots and dashes, holds a significant place in the history of communication. But why was Morse code invented in the first place?
Delving into the origins of this timeless system reveals a fascinating journey of innovation and necessity. From its humble beginnings to widespread adoption across continents, Morse code has shaped how we communicate. In this article, we unravel the story behind the Morse code’s invention, exploring the key factors that led to its creation and its impact on society.
By understanding the context and motivations behind Morse code’s development, we gain insight into its enduring relevance and significance in the modern world.
Join us as we uncover the facts and delve into the intriguing history of Morse code invented, shedding light on the ingenuity and foresight that gave rise to this remarkable communication method.
What is Morse Code?
Morse code transmits text information using a series of dots, dashes, and spaces. It was developed in the early 1830s by Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail for use with telegraph systems.
Each character in the Morse code represents a unique combination of dots and dashes, which encode letters, numbers, punctuation marks, and other symbols. Morse code can be transmitted using sound, light, or touch, making it adaptable to various communication mediums.
The simplicity and efficiency of Morse code invented made it an essential tool for long-distance communication before the advent of modern telecommunications technologies.
Despite the advancement of communication systems, Morse code remains relevant today in specific applications, such as aviation, amateur radio, and emergency signaling.
Its widespread use in the past and continued relevance in specialized fields highlight the enduring legacy of Morse code as a foundational element of human communication.
Why Was Morse Code Invented?
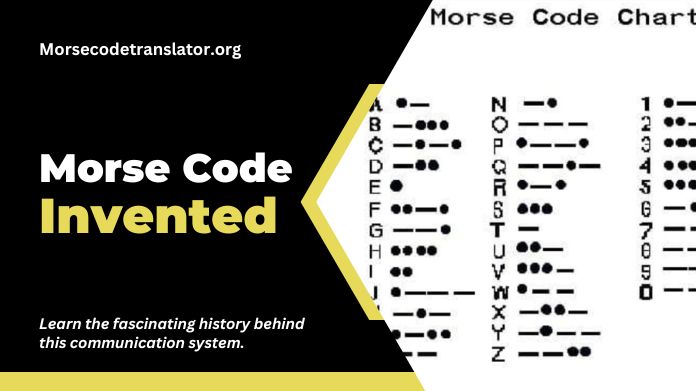
Morse code invented to facilitate long-distance communication, particularly for telegraph systems. Its invention stemmed from the need to transmit messages quickly and efficiently over electric telegraph wires.
Samuel Morse and his collaborator Alfred Vail developed Morse code in the 1830s to encode letters, numbers, and punctuation marks into a series of dots and dashes.
The invention of Morse code was motivated by the growing demand for rapid communication over long distances, particularly in the context of expanding railroads, shipping routes, and other forms of transportation.
Before the advent of Morse code, communication over long distances was limited to methods such as semaphore flags or visual signals, which were slow and prone to errors.
Morse code revolutionized communication by enabling messages to be transmitted almost instantaneously over telegraph lines. Its adoption facilitated the growth of telegraph networks worldwide and played a crucial role in connecting people and businesses across vast distances.
As a result, Morse code became an indispensable tool in telecommunication and laid the groundwork for modern forms of long-distance communication.
Application of More Code
Morse code has been applied in various fields throughout history owing to its simplicity, versatility, and reliability. Some notable applications of Morse code include:
1. Telegraphy: Morse code was initially developed for use with telegraph systems, allowing messages to be transmitted over long distances via electrical telegraph wires. It revolutionized communication by enabling the rapid transmission of information across continents.
2. Maritime Communication: Morse code played a crucial role in maritime communication, particularly in ship-to-ship and ship-to-shore communication. It was used for distress signals, navigation, and coordination among vessels at sea.
3. Aviation: Morse code was widely used for radio communication between aircraft and ground stations. Pilots and air traffic controllers transmitted coded messages to convey critical information such as weather updates, flight instructions, and emergency alerts.
4. Military Communication: Morse code has a long history of use in military communication, dating back to its deployment in wartime telegraphy during the 19th century. It was utilized for encrypted messaging, signaling, and coordination among military units on the battlefield.
5. Amateur Radio: Morse code remains popular among amateur radio operators, who use it for long-distance and emergency communication networks. Many amateur radio enthusiasts continue to practice and master Morse code as a means of communicating with fellow operators around the world.
6. Emergency Signaling: Morse code has been employed for emergency signaling in situations where other forms of communication are unavailable or compromised. It has been used by stranded hikers, mariners in distress, and individuals in remote locations to signal for help using flashlights, mirrors, or sound.
Overall, Morse code has left a lasting legacy in the field of communication, with its applications ranging from early telegraphy to modern-day emergency communication systems.
Despite the advent of advanced technologies, Morse code continues to be valued for its simplicity, efficiency, and resilience in transmitting critical information across diverse settings.
Final Note
The invention of Morse code marked a significant milestone in the history of communication. Born out of the need for efficient long-distance communication, Morse code revolutionized how messages were transmitted and paved the way for modern telecommunications systems.
Developed by Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail in the 1830s, Morse code enabled rapid encoding and decoding of messages using a series of dots and dashes. Its simplicity, versatility, and reliability made it an indispensable tool for telegraphy, maritime communication, aviation, and military operations.
Despite the advancements in communication technology since its inception, Morse code remains relevant in various specialized fields and continues to be appreciated for its enduring legacy.
The invention of Morse code facilitated the rapid exchange of information across vast distances and laid the foundation for the interconnected world we live in today.
As we reflect on its significance, we recognize Morse code as a testament to human ingenuity and innovation in overcoming the barriers of time and space through communication.
