In the intricate world of Morse Code, each dot and dash tells a silent story, transcending language barriers with a series of simple yet profound signals.
As we delve into the fascinating realm of “Morse Code Logic: Alphabet, Numbers, Punctuation & Other Characters,” we embark on a journey through the code’s intricate tapestry.
Beyond its historical roots in telegraphy, Morse Code serves as a timeless language of communication, utilizing combinations of dots and dashes to represent letters, numbers, and punctuation.
Join us as we unravel the logic behind this elegant system, exploring how a seemingly modest arrangement of signals has played a pivotal role in shaping communication throughout history and continues to do so in various modern applications.
What is Morse Code?
Morse Code is a technique of communication that utilizes a series of dots and dashes to represent letters, numbers, and punctuation marks. Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail developed it in the early 1830s for use with the newly invented telegraph.
Each letter of the alphabet, as well as numbers and special characters, is represented by a unique combination of short and long signals. Morse Code was widely used for long-distance communication before the advent of the telephone and is still used today in some specialized applications.
What is Morse Code Logic?
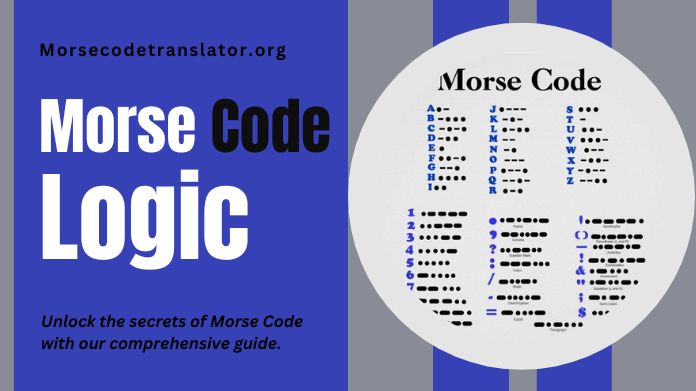
Morse Code Logic refers to the communication system created by Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail in the early 19th century. It encodes letters and numbers into a series of dots and dashes, which can then be transmitted through various means such as sound, light, or radio signals.
A unique combination of short and long signals represents each letter or number, allowing for efficient and reliable communication over long distances. Morse Code Logic played a crucial role in telegraphy and continues to be used in some communication regions today.
Features of Morse Code
Morse Code is a communication system that combines dots and dashes to represent letters and numbers. Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail developed it in the 1830s and 1840s.
Here are some key features of Morse Code:
1. Dots and Dashes: Morse Code comprises short and long signals called dots. A specific sequence of dots and dashes represents each letter and number.
2. Alphabet and Numbers: Morse Code can represent all the letters of the alphabet, as well as numbers from 0 to 9. Each character has a unique combination of dots and dashes.
3. International Usage: Morse Code is an international communication system that can be understood across different languages and cultures. Amateur radio operators, military personnel, and aviation professionals use it.
4. Distinctive Patterns: Morse Code is designed to have distinctive patterns for each character to ensure accurate communication even in noisy or low visibility conditions.
5. Versatility: Morse Code can be transmitted using various methods, including sound signals, light signals, or written symbols. It can be sent using a telegraph machine, flashlight, or tapping on a surface.
6. Efficiency: Morse Code is known for transmitting messages efficiently. By using a simple binary system of dots and dashes, it can convey information quickly and effectively.
7. Recognizable Sounds: Morse Code has distinct sounds that make it easily recognizable. For example, the letter “S” is represented by three short dots, while “O” is defined by three longer dashes.
8. Morse Code Prosigns: Besides numbers, Morse Code also includes prosigns, which are unique to convey specific meanings or instructions. Examples of prosigns include “SOS” (an international distress signal) and “AR” used to indicate the end of a transmission).
9. Historical Significance: Morse Code played a crucial role in long-distance communication before the invention of modern telecommunications systems. It was widely used in telegraphy and maritime communication, helping to connect people across vast distances.
10. Continued Relevance: Morse Code remains relevant today despite technological advancements. It is still used in specific fields, such as aviation and amateur radio, and many people continue to learn and use Morse Code as a hobby or for emergency communication purposes.
Conclusion
Morse Code is a secret language where dots and dashes tell a silent tale. In our exploration of “Morse Code Logic: Alphabet, Numbers, Punctuation & Other Characters,” we’re diving into this relaxed code.
It’s not just about history but how dots and dashes become letters, numbers, and punctuation marks. It’s a simple system that’s been a big deal in communication.
So, join us in decoding the logic behind Morse Code and discover how this neat arrangement of signals has been a language of its own, telling stories silently for a long time.
